SEDIMENT & MUCK REDUCTION
HOW DOES EUTROPHICATION CAUSE EXCESSIVE ORGANIC MUCK & SEDIMENT ACCUMULATION?
Eutrophication is a process that leads to the accumulation of excessive organic nutrient-rich muck and sediment in water bodies, driving oxygen depletion and nutrient recycling. As nutrient inflows increase due to human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and wastewater and septic system discharge, algae blooms occur.
When more phytoplankton is produced than the food web can consume, the excess algae cells die off and sink to the bottom. As these dead cells decompose, they deplete oxygen from the bottom of the water column, creating a hypoxic environment that cannot support the animal life necessary for nutrient clearing.
Positive feedback loops are established where the process entrenches itself and makes things worse as it progresses. This leads to the accumulation of nutrient-rich organic sediment, which further fuels the growth of invasive weeds, algae, and toxic cyanobacteria through nutrient recycling.
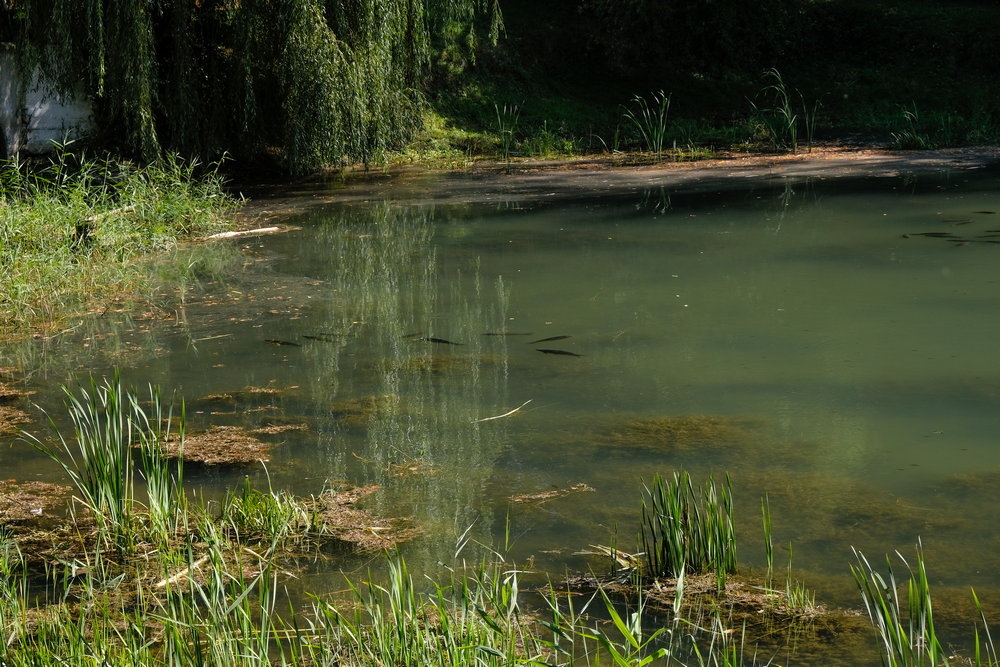

IS SEDIMENT & MUCK ACCUMULATION A PROBLEM, AND IS IT IMPORTANT?
Sediment and muck accumulation is a significant problem in eutrophic water bodies because it perpetuates the cycle of eutrophication. The nutrient-rich sediment provides a perfect rooting bed for invasive weeds and continues to recycle nutrients into the water column, sustaining algae blooms and the growth of toxic cyanobacteria.
When they die off, the sink to the bottom and decompose, depleting oxygen and causing hypoxia as they do so. This leads to a progressive deterioration of water quality, loss of biodiversity, and the impairment of the ecosystem’s ability to clear nutrients and maintain a healthy balance.
Getting rid of accumulated mucky sediment is crucial to breaking the vicious feedback loop of eutrophication and restoring the natural nutrient clearing capacity of the water body.
WHAT IS THE WRONG WAY TO GO ABOUT TRYING TO FIX THE PROBLEM?
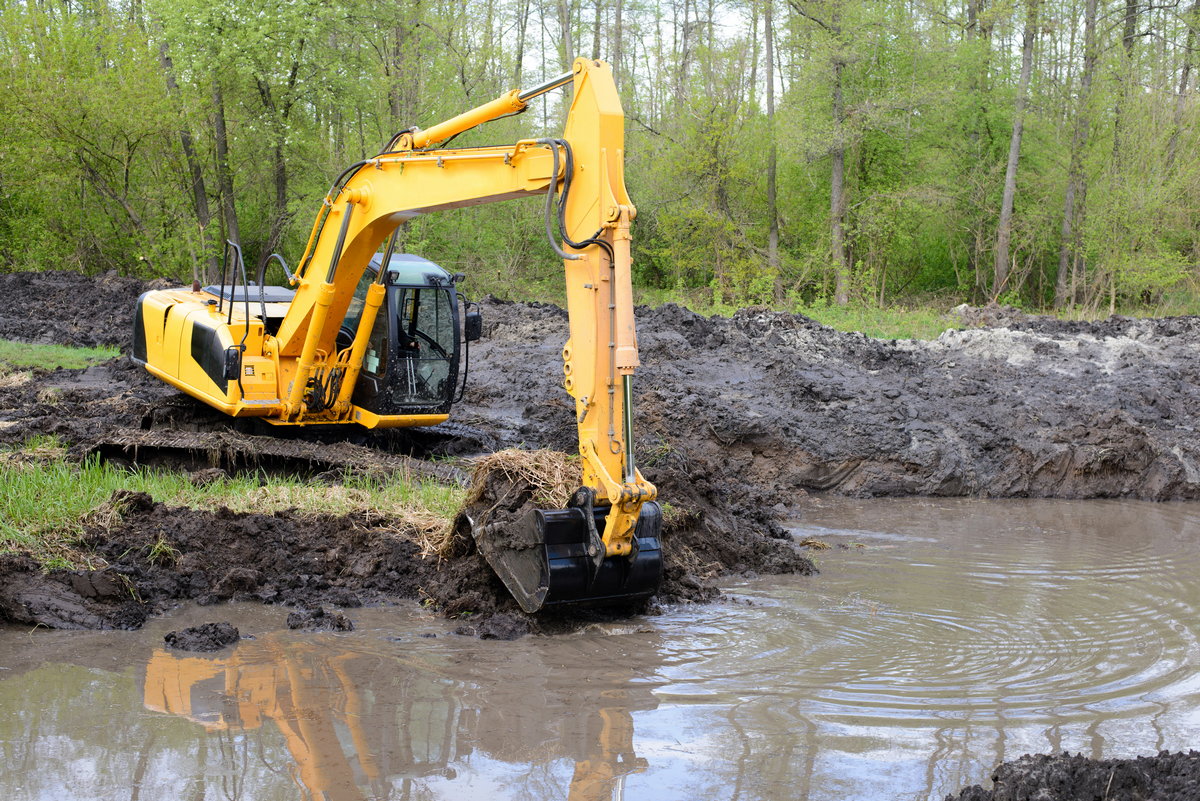

Nutrient-rich organic sediments cause further problems because they provide a perfect rooting bed for invasive weeds and recycle nutrients to fuel algae blooms.
One of the worst things you can do is use herbicides and algaecides to kill off weeds and algae because this biomass dies off, sinks to the bottom, and decomposes to produce more mucky sediment, making the situation worse.
Another often misguided approach is to dose with microbes in the hope that they will consume the mucky sediment. The problem is that such microbes are aerobic, so if the sediment-water interface is hypoxic, they will rapidly die of and become a waste of money.
Furthermore, the use of microbes stems from wastewater treatment practices where the growth of microbes is facilitated so that they proliferate to produce a microbial sludge. The point is that in a wastewater treatment plant there are processes and
the means to separate off that sludge for further treatment. In a lake if your microbes successfully proliferate and produce sludge you are making the situation worse not better.
Physical dredging is not necessarily “wrong,” but it is much more expensive, creates a lot of mess, requires heavy trucks to drive up and down roads not designed for them to haul the dredged material away, and tends to stir up sediment and mobilize nutrients that cause algae blooms.
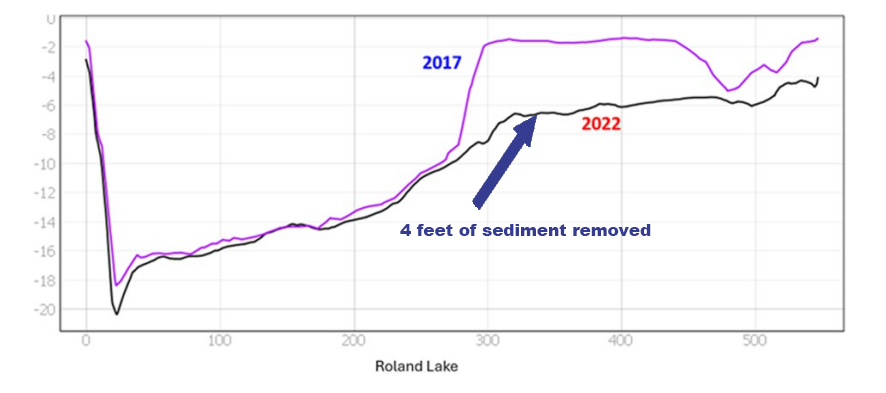
HOW DO YOU FIX MUCK & SEDIMENT ACCUMULATION?
Our approach to dealing with excessive muck and organic sediment accumulation is Bio-Dredging – a clean, efficient, and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional dredging.
It involves the use of RADOR oxygenation technology to ensure that the benthic margin, where water meets sediment, is fully oxygenated, and digestive enzymes that work efficiently in the oxygenated environment to break down the sediment.
By gradually working off the accumulated muck and sediment nutrient stockpiles, Bio-Dredging helps stop the perpetual recycling of nutrients that fuels algae and cyanobacteria growth, thereby promoting the restoration of a healthy, balanced ecosystem.
This approach focuses on addressing the root causes of eutrophication, such as oxygen depletion, muck accumulation, sediment nutrient recycling, and the impairment of the food web, to break the positive feedback loops that continue to worsen the situation.
Download the Lake Management ACTION Plan E-Book
Ready to explore how oxygenation can transform your lake? Download Clean-Flo’s Lake Management ACTION Plan E-Book to learn more about our innovative solutions, real-world results, and how we can help restore and protect your lake.
